
- #Java reflection to serialize full
- #Java reflection to serialize android
- #Java reflection to serialize code
- #Java reflection to serialize free
It can make transitions or rotation from portrait to landscape feel very sluggish. If you are trying to pass a list with thousands of serialized objects, it is possible that the whole process will take more than a second.
#Java reflection to serialize free
Feel free to use it but remember that serialization is an expensive operation so keep it to a minimum. However, in most cases, the slowness of Serializable won’t be noticeable. If you want to be a good citizen, take the extra time to implement Parcelable since it will perform 10 times faster and use less resources. How do you serialize and retrieve structured data like this There are a few ways to solve this problem: Use Java Serialization.
#Java reflection to serialize full
There you have it: Parcelable is more than 10x faster than Serializable! It is also interesting to note that even on a Nexus 10, a pretty simple object can take about 1 millisecond to go through a full serialize/deserialize cycle.

#Java reflection to serialize android
#Java reflection to serialize code
There is a significant amount of boilerplate code and it makes the classes harder to read and maintain. However, it is obvious here that implementing Parcelable is not free. In Java Serialization, a record class is made serializable just like a normal class, by implementing java.io.Serializable. It also stands to reason that the code has been heavily optimized for this purpose. One of the reasons for this is that we are being explicit about the serialization process instead of using reflection to infer it. access modifiers, accessors and constructors omitted for brevity public class SerializableDeveloper implements Serializable String name int yearsOfExperience List skillSet float favoriteFloat static class Skill implements Serializable Īccording to google engineers, this code will run significantly faster. To answer this, lets take a look at both approaches. Looking at the api, we realize that we have two options, we can either make our objects Parcelable or Serializable. As Java developers, we already know of the Serializable mechanism, so why bother with Parcelable? Employee class implement Serializable interface.When starting on Android, we all learn that we cannot just pass object references to activities and fragments, we have to put those in an Intent / Bundle. Create classes implementing TableEntity to customize property storage, retrieval, serialization and deserialization, and to provide additional custom. The TableEntity interface declares getter and setter methods for the common entity properties, and and methods for serialization and deserialization of all entity properties using a property map. Given below is an example Java program to save an arraylist of Employee objects. An interface required for table entity types. Example to serialize ArrayList of objects The list is serialized in project root folder. ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos) Public static void main(String args) throws ExceptionįileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("listData") Given below is an example Java program to persist an arraylist of strings. Example to serialize ArrayList of strings Note – The elements stored in arraylist should also be serializable, else program will throw NotSerializableException.
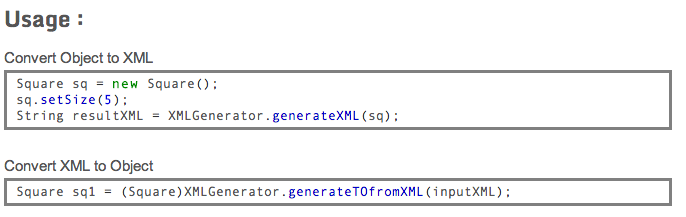
We can directly use ObjectOutputStream to serialize ArrayList, and ObjectInputStream to deserialize an arraylist object. It essentially means that we do not need to implement Serializable interface explicitly in order to serialize ArrayList. In Java, ArrayList class is serializable by default.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
